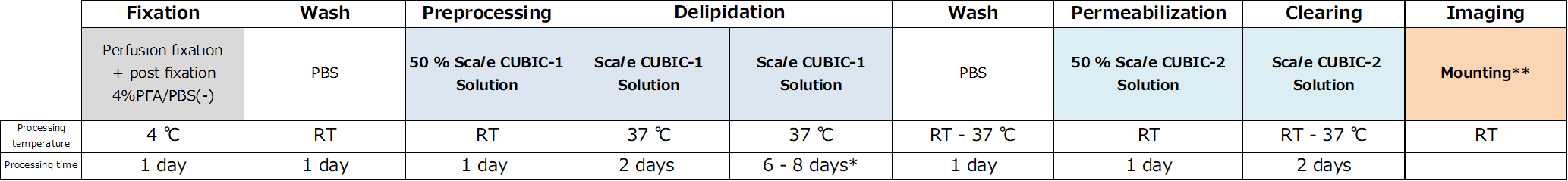
Wako 290-80801 CUBIC Trial Kit CUBIC试剂盒
CUBIC Trial Kit
Tissue Optical Clearing Reagent Manufacturer : FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical Corporation Storage Condition : Keep at RT.
This product is for research use only. Do not administer it to human.
CUBIC Trial Kit is the reagent kit used for CUBIC (Clear, Unobstructed Brain/Body Imaging Cocktails and Computational analysis) that is clearing method. This method was developed by Professor Hiroki Ueda and Associate Professor Etsuo Susaki etc.
A tissue can be made transparent only soaking into ScaleCUBIC-1 and ScaleCUBIC-2 included in the kit. Also, it’s possible to adjust RI and make microscopic observation by using a reagent that is mixed Mounting Solution-1 and Mounting Solution-2 included the kit. Mouse whole brain can be made transparent in 2 weeks.
CUBIC enables transparency and observation mouse whole tissue including brain, primates such as marmosets whole brain and fish or crustacean whole tissue. This method is expected to be applied pathological approach or to observation of single cell level.
本产品仅供研究使用。 不要将其施用于人类。
CUBIC Trial Kit 是用于 CUBIC (Clear, Unobstructed Brain/Body Imaging Cocktails and Computational analysis) 的试剂盒,是一种清除方法。 该方法由上田博树教授和须崎悦男副教授等开发。
只有浸泡在套件中包含的 ScaleCUBIC-1 和 ScaleCUBIC-2 中才能使组织透明。 此外,通过使用试剂盒中包含的 Mounting Solution-1 和 Mounting Solution-2 混合的试剂,可以调整 RI 并进行显微观察。 小鼠全脑可在 2 周内变得透明。
CUBIC 可实现透明和观察小鼠全组织,包括大脑、灵长类动物(如狨猴全脑和鱼类或甲壳类动物全组织)。 该方法有望应用于病理方法或单细胞水平的观察。
Whole-brain / body imaging with single-cell resolution
CUBIC
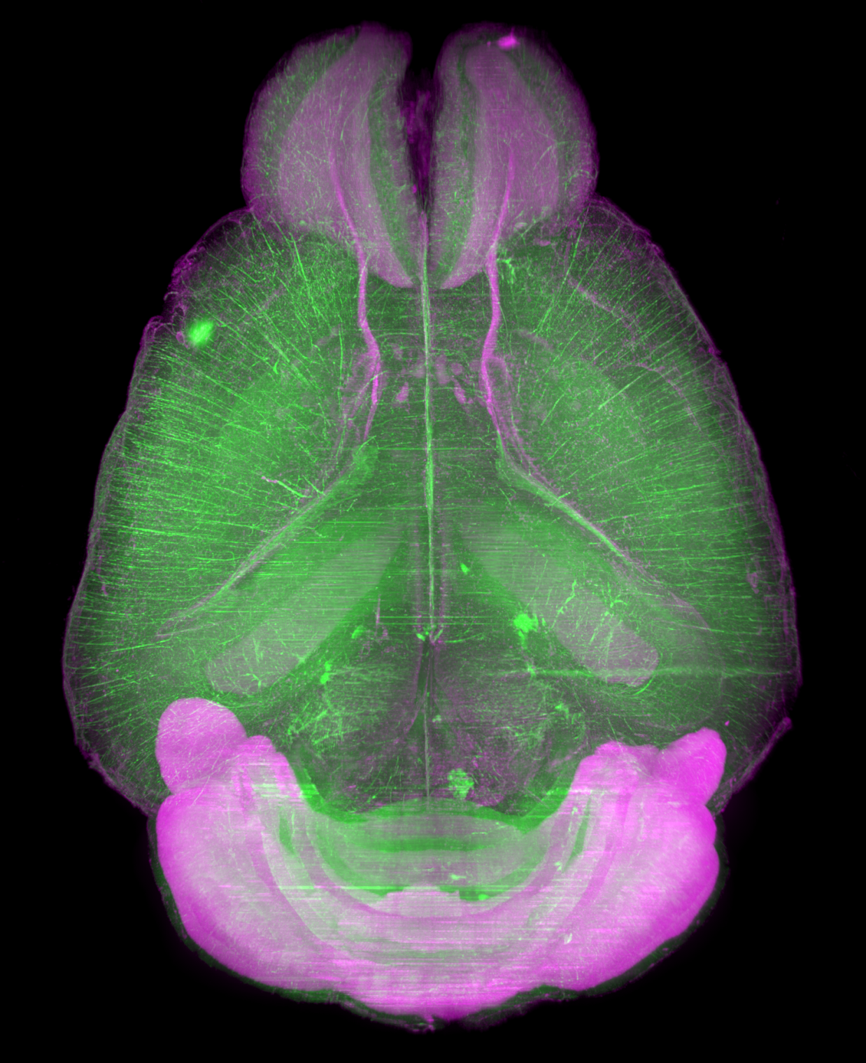
Dr. Hiroki R. Ueda et al. developed a simple, efficient, and scalable brain / body clearing method and imaging / computational analysis pipeline, CUBIC (clear, unobstructed brain/body imaging cocktails and computational analysis). CUBIC offers a fluorescent-preserving, high-performance and device-free tissue clearing method based on hydrophilic Solutions (ScaleCUBIC Solutions).
It enables reproducible whole-organ and whole-body clearing and rapid 3D imaging with LSFM. CUBIC also provides processing and analysis of 3D images for extracting biological information.
Therefore, CUBIC presents a platform of whole-organ/body imaging with single-cell resolution and image informatics, which enables a wide range of users to perform experiments targeting cellular and organ layers with multiple samples..
Data provided by Dr. Etsuo A Susaki, and Dr. Hiroki R. Ueda, RIKEN
Features
- Easy-to-use
- No special equipment required
- Follow up 2D H&E
- High transparency
- Applicable for many organs
- Compatible with IF, FP and other fluorescent labels
Protocol
Whole organ samples
2 mm section samples
Fluorescent protein expression tissue
Whole organ samples
 **Typically, 3:7 mixture of Mounting Solution 1 and 2 (RI ~1.49) can be used.
**Typically, 3:7 mixture of Mounting Solution 1 and 2 (RI ~1.49) can be used.
| Brain | Heart | Lung | Kindney | Liver | |
| PBS | 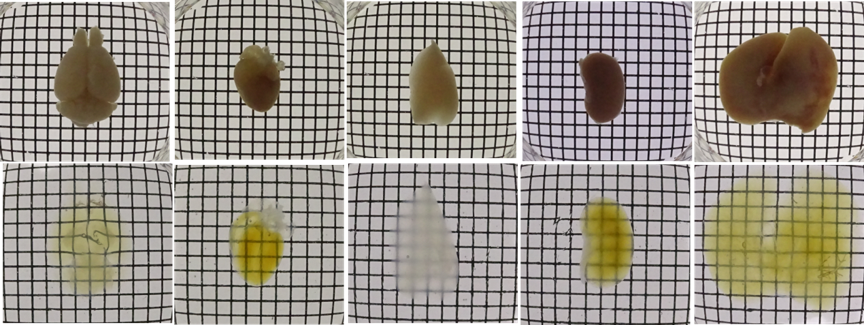 |
||||
| CUBIC | |||||
Figure1.Transmittance images of mouse whole organs before and after clearing with Scale CUBIC Solutions.
2 mm section samples
**Typically, 3:7 or 2:8 mixture of Mounting Solution 1 and 2 (RI ~1.49) can be used
| Brain | Heart | Liver | |
| PBS | 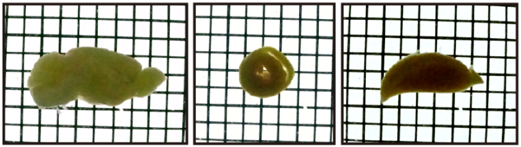 |
||
| CUBIC | 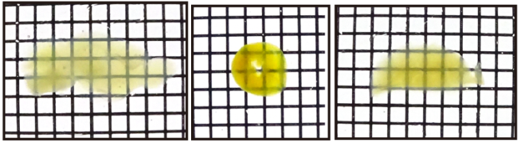 |
||
Figure2.Transmittance images of mouse 2mm slices before and after clearing with Scale CUBIC Solutions.
Fluorescent protein expression tissue

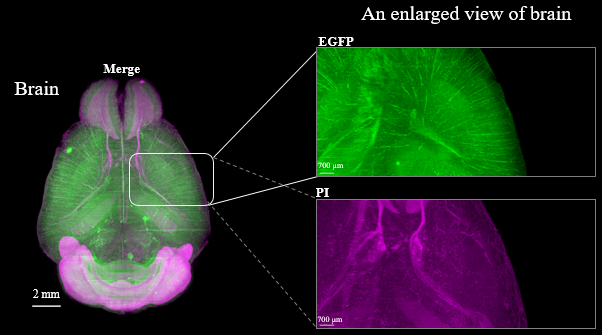
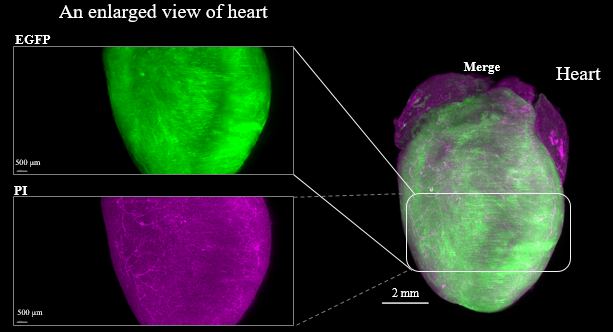
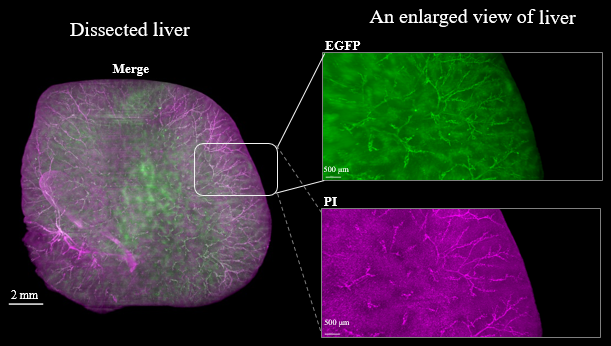 Figure3. LSFM imaging of CAG-EGFP Tg Mouse (8w Male) whole brain, whole heart and dissected liver.
Figure3. LSFM imaging of CAG-EGFP Tg Mouse (8w Male) whole brain, whole heart and dissected liver.
Application
CUBIC Application with pathological methods
CUBIC Application with fish clearing
CUBIC Application with crustacean clearing
CUBIC Application with beetle clearing
Visualization of whole-brain vascular networks
CUBIC Application with pathological methods
Data by S. Nojima.et al. : Scientific Reports ,7,9269 (2017) / Adapted.
| Before CUBIC
|
After CUBIC ——————————————————————————————- |
||||||
| 0 day | 2 days | 3 days | 4 days | 6 days | 7 days | ||
| Human lung |
CUBIC | 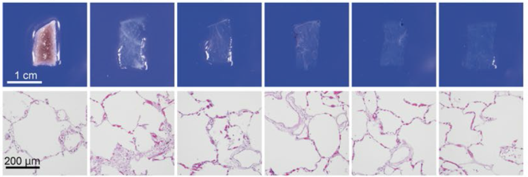 |
|||||
| HE stain | |||||||
| Human Lymph node |
CUBIC | 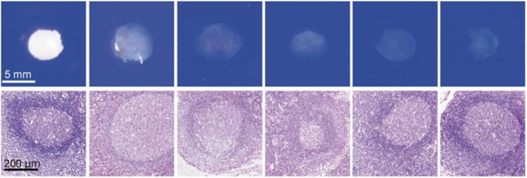 |
|||||
| HE stain | |||||||
Figure 4.Tissue clearing of various human organs with CUBIC
Tissue clearing and 3D imaging of deparaffinizedsamples with CUBIC
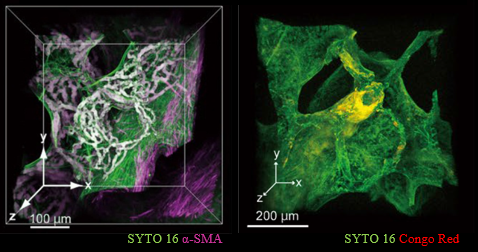 Figure 5.Tissue clearing and 3D imaging of pathological specimens with CUBIC.
Figure 5.Tissue clearing and 3D imaging of pathological specimens with CUBIC.
CUBIC Application with fish clearing
Data were provided by Kunihiko Futami, Tokyo University of Marine Science and Technology.

Figure6. Fish clearing with CUBIC
See Reference 5) for the protocol
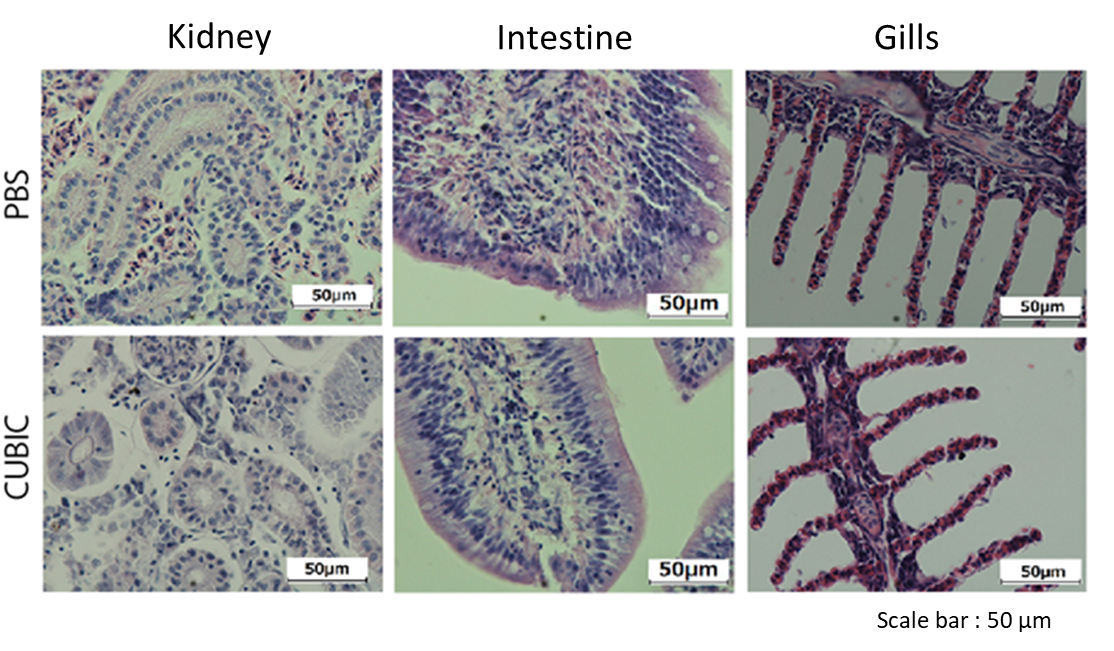
Figure7. Stained image of Fish organ treated by CUBIC
Organs were sliced at 5 μm and stained with Mayer’s hematoxylin after CUBIC treatment.
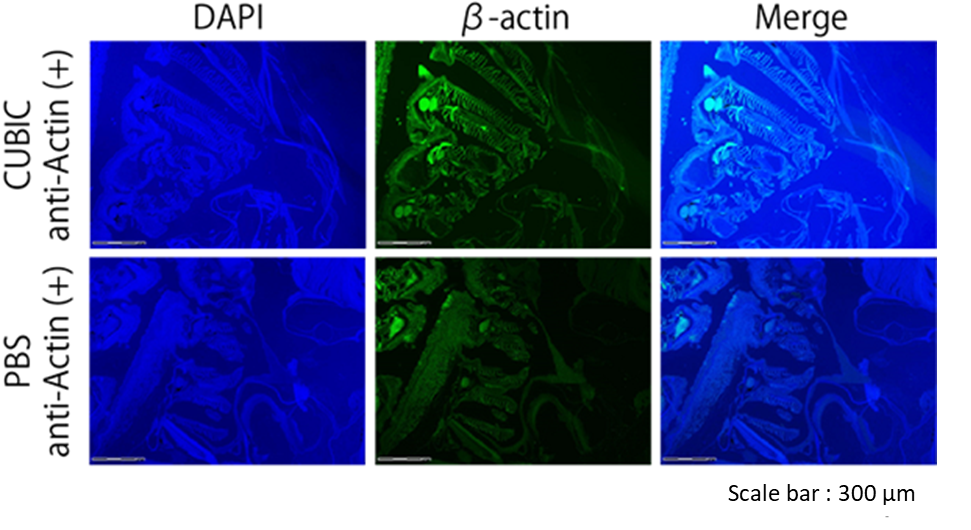
Figure8. Immunostaining image of zebrafish treated with CUBIC
CUBIC Application with crustacean clearing
Data were provided by Aru Konno and Shigetoshi Okazaki, Hamamatsu University School of Medicine in Japan.
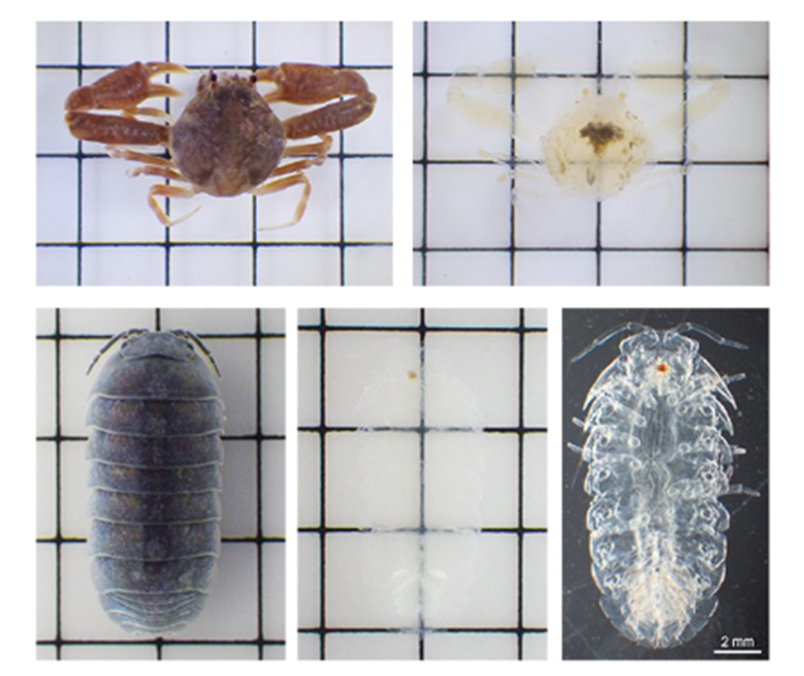

Figure9. Crustacean clearing with CUBIC
See Reference 6) for the protocol
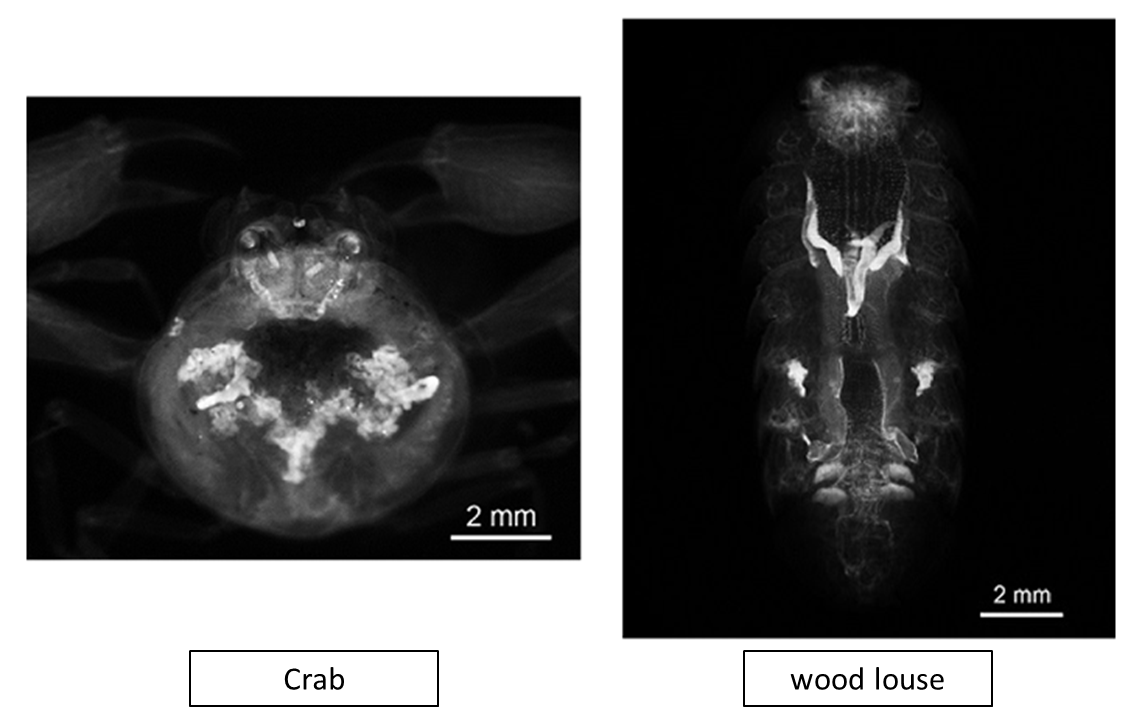
Figure10. Crustacean clearing with CUBIC (PI staining)
See Reference 6) for the protocol
CUBIC Application with beetle clearing
Data were provided by Shinya Kuroda, Tokyo University
Beetle clearing requires fixing, bleaching, and clearing steps.
See the website for Detailed protocols.
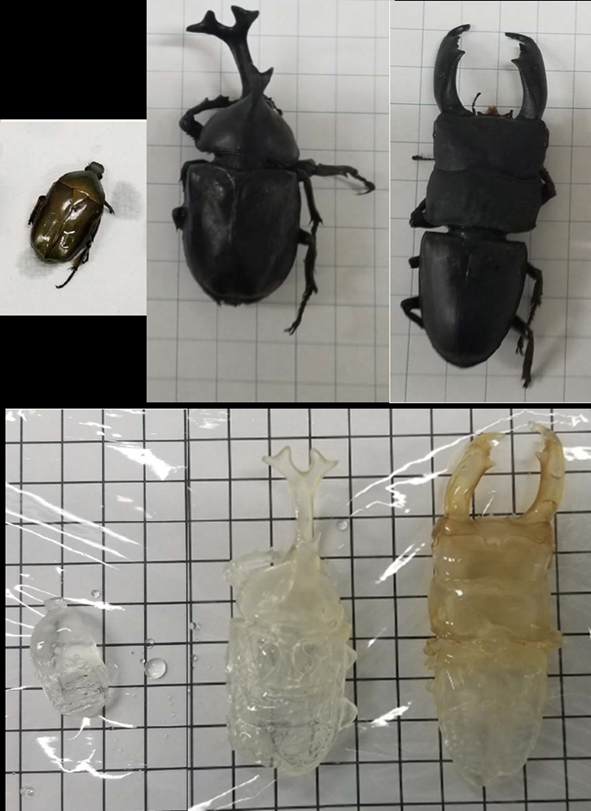 Figure11. Beetle clearing with CUBIC
Figure11. Beetle clearing with CUBIC
LEFT: drone beetle MIDDLE: rhinoceros beetle RIGHT: stag beetle
This protocol altered from reference 7).
Visualization of whole-brain vascular networks
Data by Miyawaki, T. et al. : Nat. Commun., 11:(1) (2020)
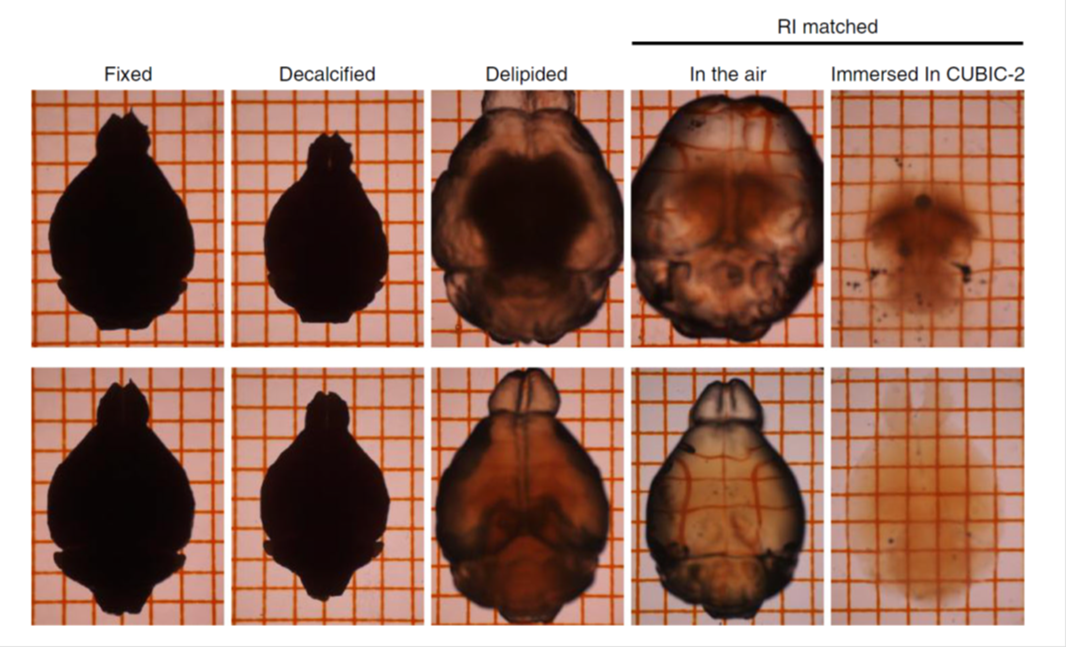
Figure12. Tissue clearing with sodium deoxycholate (SDC)
TOP: SDS-based delipidation. The tissue was swelling.
BOTTOM: SDC-based delipidation. Tissue swelling was suppressed.
This protocol altered from reference 8).
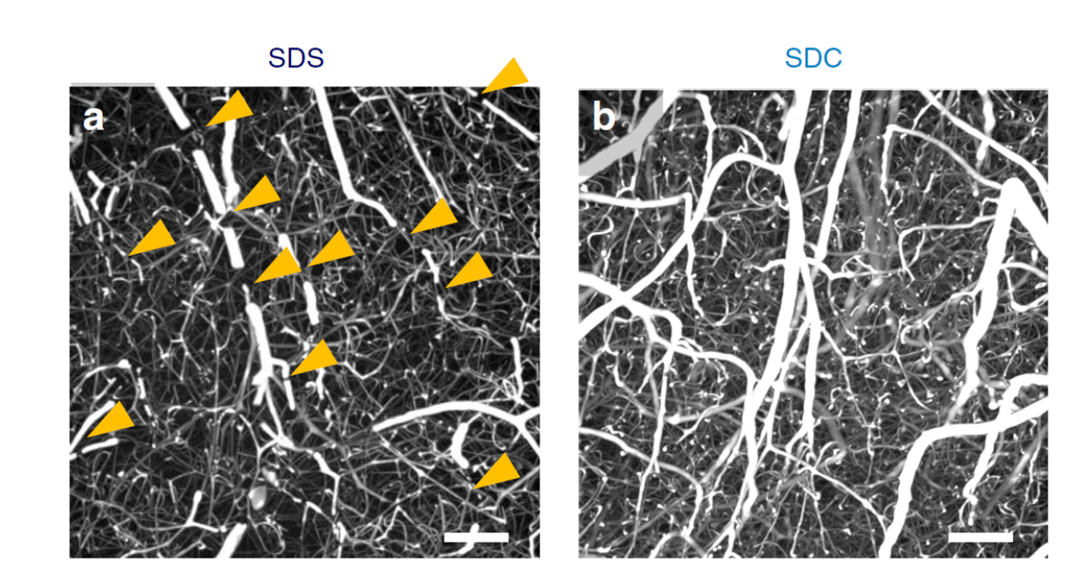
Figure13. Mouse brain cortex clearing after vascular casting
LEFT: SDS-based delipidation. Some penetrating vessels were severed (arrowheads).
BOTTOM: SDC-based delipidation. Breakages of vessels were rarely.
This protocol altered from reference 8).
References 参考文献
- E. A. Susaki. et al. : Cell, 157(3), 726 (2014).
- K. Tainaka. et al. : Cell, 159(4), 911 (2014).
- E. A. Susaki. et al. : Nature Protocols, 10, 1709 (2015).
- S. Nojima. et al. : Scientific Reports, 7, 9269 (2017).
- S. Ohnuma. et al.: Fish Pathology, 52(2), 96(2017).
- A. Konno and S. Okazaki.: Zoological Letters, 4:13(2018).
- M Kuroda and S Kuroda (2020). Whole-body clearing of beetles by successive treatment of hydrogen peroxide and CUBIC reagents.
- Miyawaki, T. et al. : Nat Commun., 27, 11(2020).